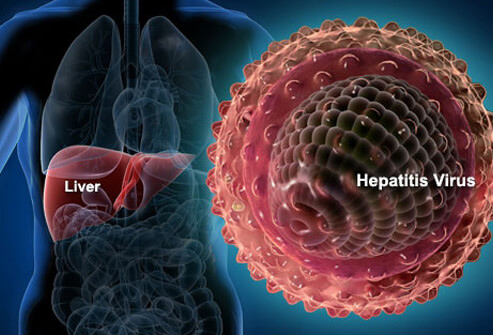
Hepatitis B is an infectious inflammatory illness of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) the disease has caused epidemics in parts of Asia and Africa. About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 350 million who are chronic carriers.
The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids such as semen and vaginal fluids, while viral DNA has been detected in the saliva, tears, and urine of chronic carriers.
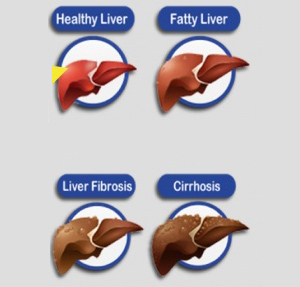
The acute illness causes liver inflammation, vomiting, jaundice and, rarely, death. Chronic hepatitis B may eventually cause cirrhosis and liver cancer—a disease with poor response to all but a few current therapies.The infection is preventable by vaccination.
Hepatitis B virus is an hepadnavirus Although replication takes place in the liver, the virus spreads to the blood where viral proteins and antibodies against them are found in infected people.The hepatitis B virus is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
Hepatitis related with virus A or E is easily curable with Ayurvedic treatment. This is known to all, however, modern medical science is still under research to counteract the virus. But Hepatitis B and C are very complicated to cure. But Ayurveda has good reputation in the treatment of liver diseases.
CAUSES OF HEPATITIS-B:
1. Sexual contact
2. Sharing needles
3. Work-related exposure: People who handle blood or instruments
4. Body piercings and tattoos
5. blood transfusions
6. Childbirth: Mother to Baby
SYMPTOMS OF ACUTE HEPATITIS-B INFECTION:
- fatigue,
- loss of appetite,
- nausea,
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and
- pain in the upper right abdomen (due to the inflamed liver).
SYMPTOMS OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS-B INFECTION:
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus either may be asymptomatic or may be associated with a chronic inflammation of the liver (chronic hepatitis), leading to cirrhosis over a period of several years. This type of infection dramatically increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). Chronic carriers are encouraged to avoid consuming alcohol as it increases their risk for cirrhosis and liver cancer.