*
Liver
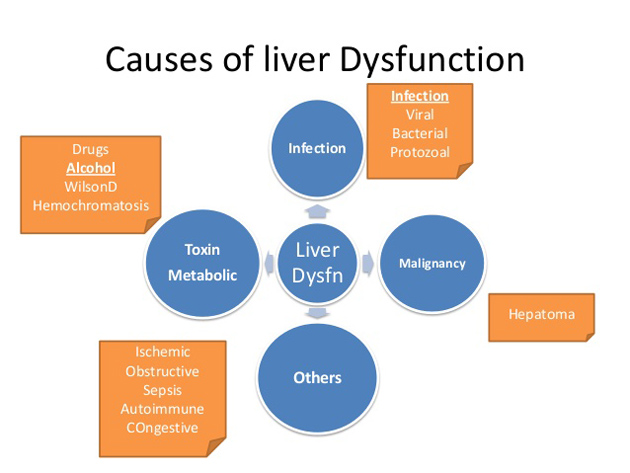
Type of Disease |
Description |
Examples of Causes/Conditions |
Acute liver failure |
Rapid decrease in liver function |
Drugs, toxins, a variety of liver diseases |
Autoimmune-associated |
The body produces an inappropriate immune response against itself; sometimes develops antibodies against own liver tissue |
PBC (Primary biliary cirrhosis), PSC (Primary sclerosing cholangitis), Autoimmune hepatitis |
Budd-Chiari syndrome |
Blood clots impede blood flow from the liver; symptoms such as ascites, enlarged liver, jaundice, and abdominal pain can develop |
Hypercoagulable disorders, liver injury, cancer,parasitic infection |
Cirrhosis |
Scarring of liver tissue leads to decreased liver function |
Can be caused by a variety of conditions but usually a result of chronic hepatitis, alcoholism, or chronic bile duct obstruction |
Genetic |
Gene mutations can lead to liver damage, disease; relatively rare conditions |
Hemochromatosis, Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson's disease |
Hepatitis |
Acute or chronic liver inflammation |
Viruses, alcohol abuse, drugs, toxins, autoimmune, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) |
Infections |
Certain infections can cause various degrees of liver damage, blockage of bile ducts |
Viral hepatitis, Parasitic infection |
Liver cancer |
A cancer that originates in the liver |
Increased risk with cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is most common primary liver tumor |
Obstruction of bile ducts |
Complete or partial blockage of bile ducts |
Tumors, gallstones, inflammation, trauma |